Image source: Canva.com
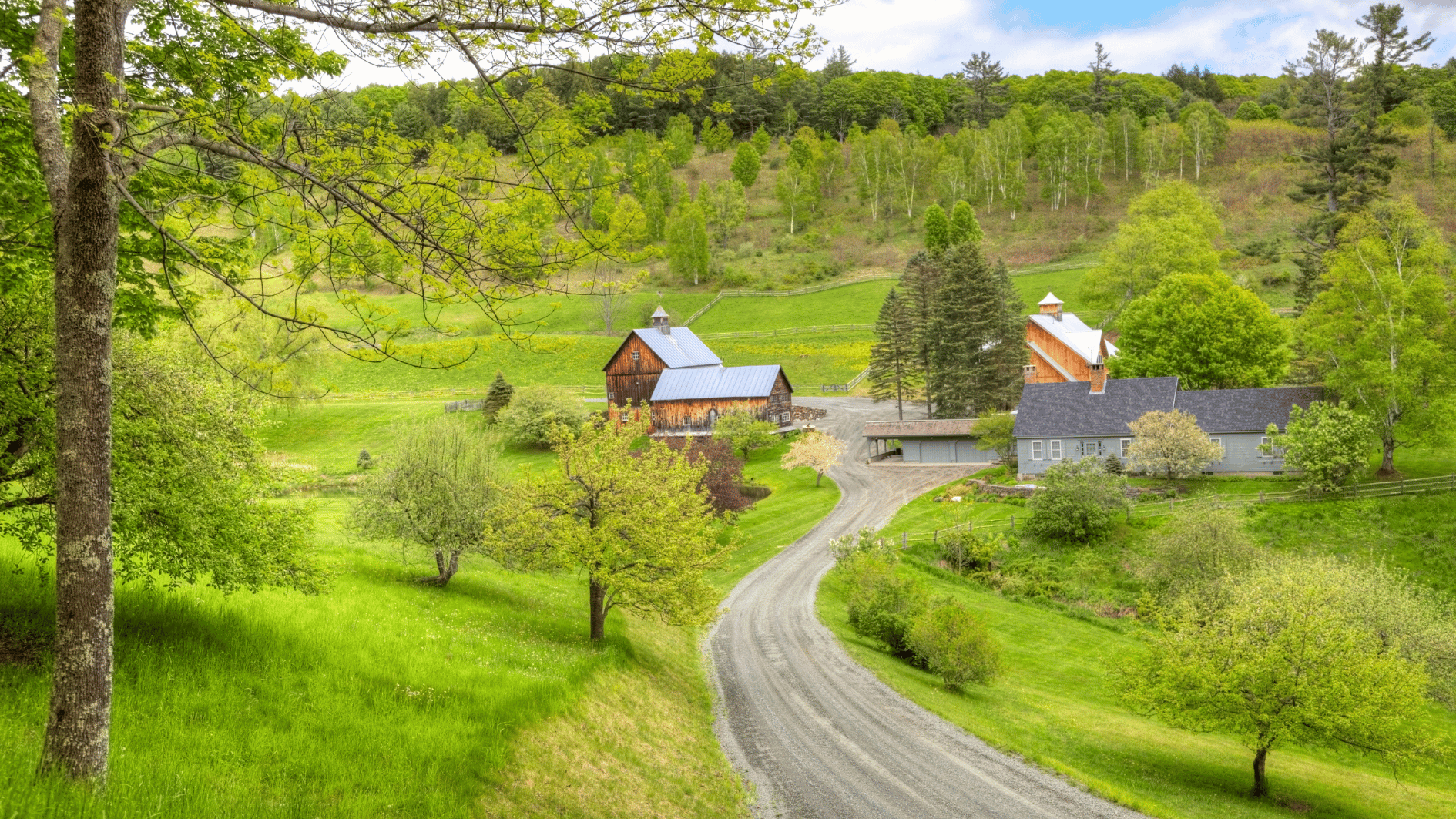
As the global push for renewable energy intensifies, solar power has emerged as a front-runner in the transition to cleaner electricity. However, the industry’s growth has been significantly influenced by government incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and rebates. With some governments scaling back or eliminating these incentives, a critical question arises: Can solar power remain competitive without government support?
The Role of Government Incentives in Solar Growth
Government incentives have played a pivotal role in making solar energy more accessible and affordable. Programs such as Clean Electricity Investment Credit (former ITC), net metering, and feed-in tariffs have encouraged both residential and commercial solar adoption. These policies have led to substantial cost reductions and technological advancements, driving rapid industry growth.
Key Benefits of Government Support

Cost Reduction
✔ Incentives help lower the upfront costs of solar installations, making them more financially viable.

Market Expansion
✔ Subsidies encourage wider adoption by reducing financial barriers for individuals and businesses.

Technological Advancement
✔ Funding for research and development accelerates innovation, improving efficiency and reducing costs.

Job Creation
✔ The solar industry has created thousands of jobs worldwide, supported by government-backed programs.
The Impact of Incentive Rollbacks
With some countries and states reducing or phasing out solar incentives, the industry faces new challenges. Without subsidies, solar companies must rely on market dynamics, private investments, and continued technological progress to remain competitive.
Potential Challenges
Higher Initial Costs
✔ Without financial aid, upfront installation costs could deter adoption.

Slower Market Growth
✔ A reduction in incentives may slow down expansion, particularly in emerging markets.

Grid Parity Concerns
✔ Achieving cost parity with traditional fossil fuels may take longer without government support.

Investment Uncertainty
✔ Policy changes create uncertainty, potentially discouraging investors from funding solar projects.
Can Solar Power Compete Without Incentives?
Despite these challenges, solar energy has seen significant cost reductions, improving its competitiveness. The cost of solar panels has declined by more than 80% over the past decade, thanks to increased production efficiencies and economies of scale. Moreover, innovations in energy storage, smart grids, and decentralized energy systems continue to enhance solar’s viability.
Factors Supporting Solar’s Competitiveness:
✔ Falling costs: Continued technological advancements and mass production have significantly reduced costs.
✔ Corporate and consumer demand: Businesses and homeowners increasingly prefer renewable energy for sustainability and cost savings.
✔ Grid independence: Advancements in battery storage allow solar users to rely less on the grid, reducing long-term costs.
✔ Policy shifts toward carbon pricing: Carbon taxes and emissions regulations favor renewable energy over fossil fuels.
The Road Ahead for Solar Energy
While government incentives have been crucial in the early stages of solar adoption, the industry is becoming increasingly self-sustaining. Many solar companies are adapting by improving efficiency, developing innovative financing models, and leveraging corporate and institutional investments. Additionally, as public awareness of climate change grows, consumer demand for clean energy remains strong.
Possible Strategies for a Post-Subsidy Era:
✅ Innovative financing: Solar leasing, power purchase agreements (PPAs), and community solar projects can help reduce upfront costs.
✅Technological improvements: Further advancements in efficiency, battery storage, and grid integration will enhance solar’s competitiveness.
✅ Corporate investment: Large companies investing in solar energy for sustainability goals can drive industry growth.
✅ Policy advocacy: While subsidies may decline, pushing for fair energy policies, such as net metering and carbon pricing, can support solar expansion.

Solar power has made remarkable progress, and while government incentives have accelerated its adoption, the industry is increasingly positioned to thrive independently. As technology continues to advance and costs decline, solar energy is poised to remain a dominant player in the global energy landscape – even without direct government support. However, strategic policy decisions and innovative business models will be crucial in ensuring its continued success in a post-subsidy world.





