Image source: Canva.com
As the demand for renewable energy grows, innovative solutions are emerging to make solar power more accessible and efficient. One such innovation is floating solar panels, also known as floating photovoltaics (FPV). These panels are installed on bodies of water rather than on land, offering unique advantages and opportunities for clean energy generation. In this article, we’ll explore what floating solar panels are, how they work, and why they are gaining attention worldwide.
What Are Floating Solar Panels?
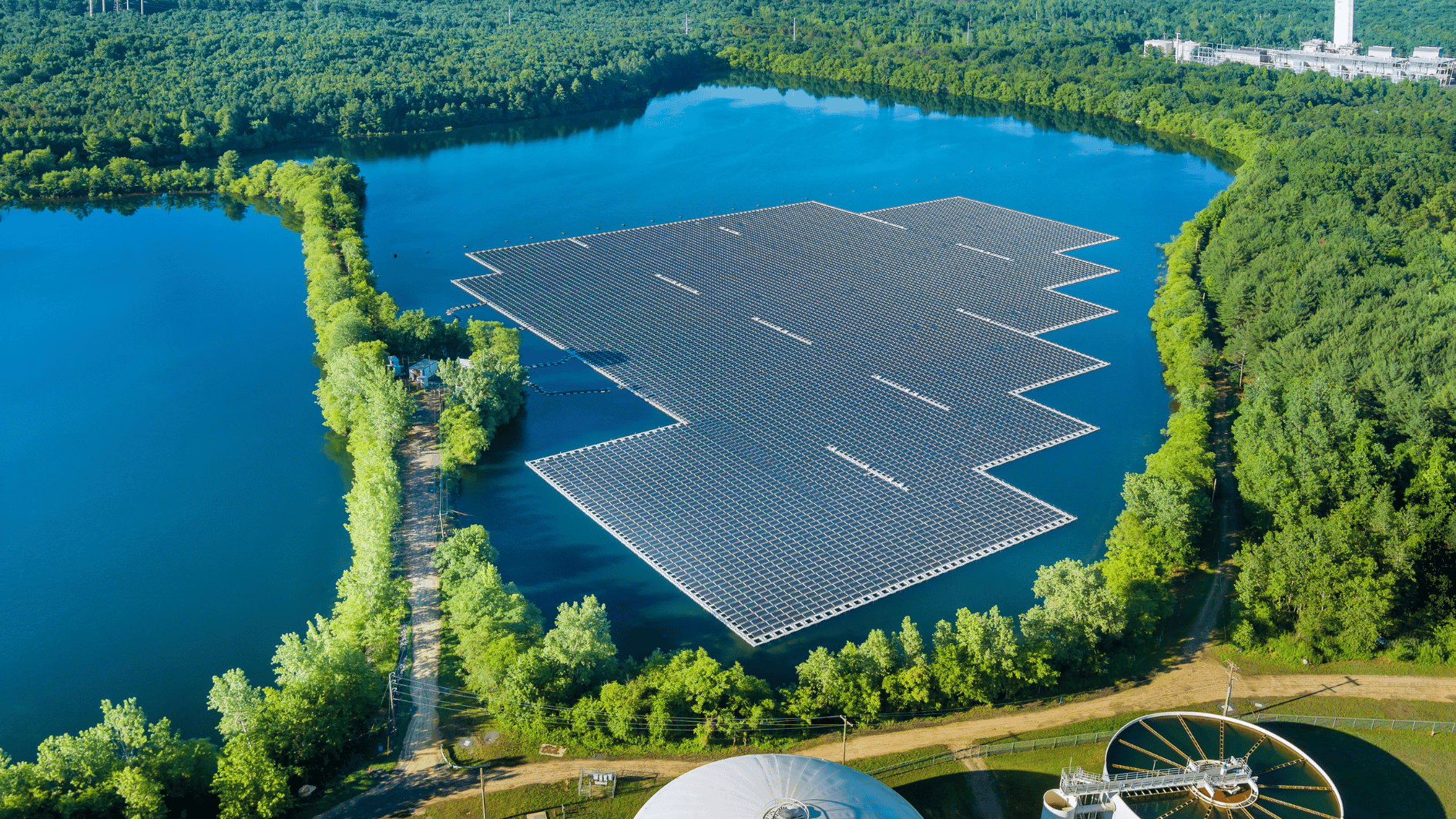
Floating solar panels are solar photovoltaic systems that are mounted on floating structures and placed on the surface of water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, ponds, or even the ocean. Instead of occupying valuable land, these panels float on water, making use of underutilized space while generating electricity from the sun.
The basic components of a floating solar system include:

Solar Panels: The photovoltaic panels that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
Floating Platforms: These are structures, often made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other durable materials, that support the solar panels on the water’s surface.
Anchoring and Mooring Systems: To keep the floating platforms in place, these systems secure the solar panels to the bed of the water body or to fixed points onshore.
Electrical Connections: Wires and cables connect the solar panels to inverters and the electrical grid, allowing the generated electricity to be used or stored.
How Do Floating Solar Panels Work?
Floating solar panels operate similarly to traditional land-based solar systems. The panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then sent to an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which can be used to power homes, businesses, or other facilities.
The floating nature of these systems provides several advantages:
Cooling Effect
Water bodies naturally help cool the solar panels, which can improve their efficiency. Solar panels typically lose efficiency as they heat up, but the cooling effect of water can mitigate this, allowing floating panels to perform better, especially in hot climates.
When installed on reservoirs or lakes, floating solar panels can reduce water evaporation by providing shade. This is particularly beneficial in regions where water conservation is a priority.
Reduced Evaporation
Dual Use of Space
Floating solar panels make use of otherwise underutilized water surfaces, preserving land for agriculture, conservation, or development. This is especially important in densely populated areas where land is scarce.
Benefits of Floating Solar Panels
Benefits of Floating Solar Panels
Floating solar panels offer several key benefits that make them an attractive option for expanding solar energy production:

Land Conservation
By placing solar panels on water, land that would otherwise be used for solar farms is freed up for other purposes. This is particularly valuable in regions where land is limited or highly prized for agriculture, development, or natural habitats.
Increased Efficiency
The cooling effect of water can enhance the performance of solar panels, leading to higher electricity output compared to land-based systems. This increased efficiency can make floating solar projects more economically viable.
Water Conservation
Floating solar panels can reduce the rate of evaporation from water bodies, helping to conserve water resources. This is a significant advantage in areas facing water scarcity or drought conditions.
Environmental Impact
Floating solar panels have a lower environmental impact compared to land-based systems. They do not require clearing large tracts of land, which can disrupt ecosystems. Additionally, the shading effect of the panels can help control algae growth in water bodies.
Scalability
Floating solar installations can be scaled up or down depending on the size of the water body and the energy needs of the area. This flexibility allows for the development of both small-scale and large-scale projects.
Challenges and Considerations
While floating solar panels offer many advantages, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
Installation and Maintenance Costs
Floating solar systems can be more expensive to install and maintain than traditional land-based systems. The cost of floating platforms, anchoring systems, and specialized installation can add to the overall expense of the project.
Environmental Impact
Although floating solar panels have a lower land impact, they can still affect aquatic ecosystems. Careful planning is needed to minimize disruption to wildlife and water quality.
Durability and Resilience
Floating solar panels must withstand harsh environmental conditions, including strong winds, waves, and potential flooding. The materials and design of the floating platforms must be robust enough to endure these challenges.
Regulatory and Permitting Issues
Installing solar panels on water bodies may require additional permits and regulatory approvals. These processes can vary by region and may add complexity to project development.
Global Adoption and Future Potential
Floating solar panels are emerging as a promising solution for expanding solar energy capacity globally. Their future potential is substantial, especially in areas with limited land or where water conservation is essential. As advancements in technology drive down costs, floating solar is expected to become a key player in the global renewable energy mix.
These systems offer an innovative approach to generating clean electricity by utilizing water surfaces, helping to preserve land and water resources. While challenges remain, the benefits of floating solar panels make them an appealing option for regions with constrained space and resources. With growing investments from countries and companies, floating solar panels are set to play a pivotal role in the transition to a sustainable energy future.