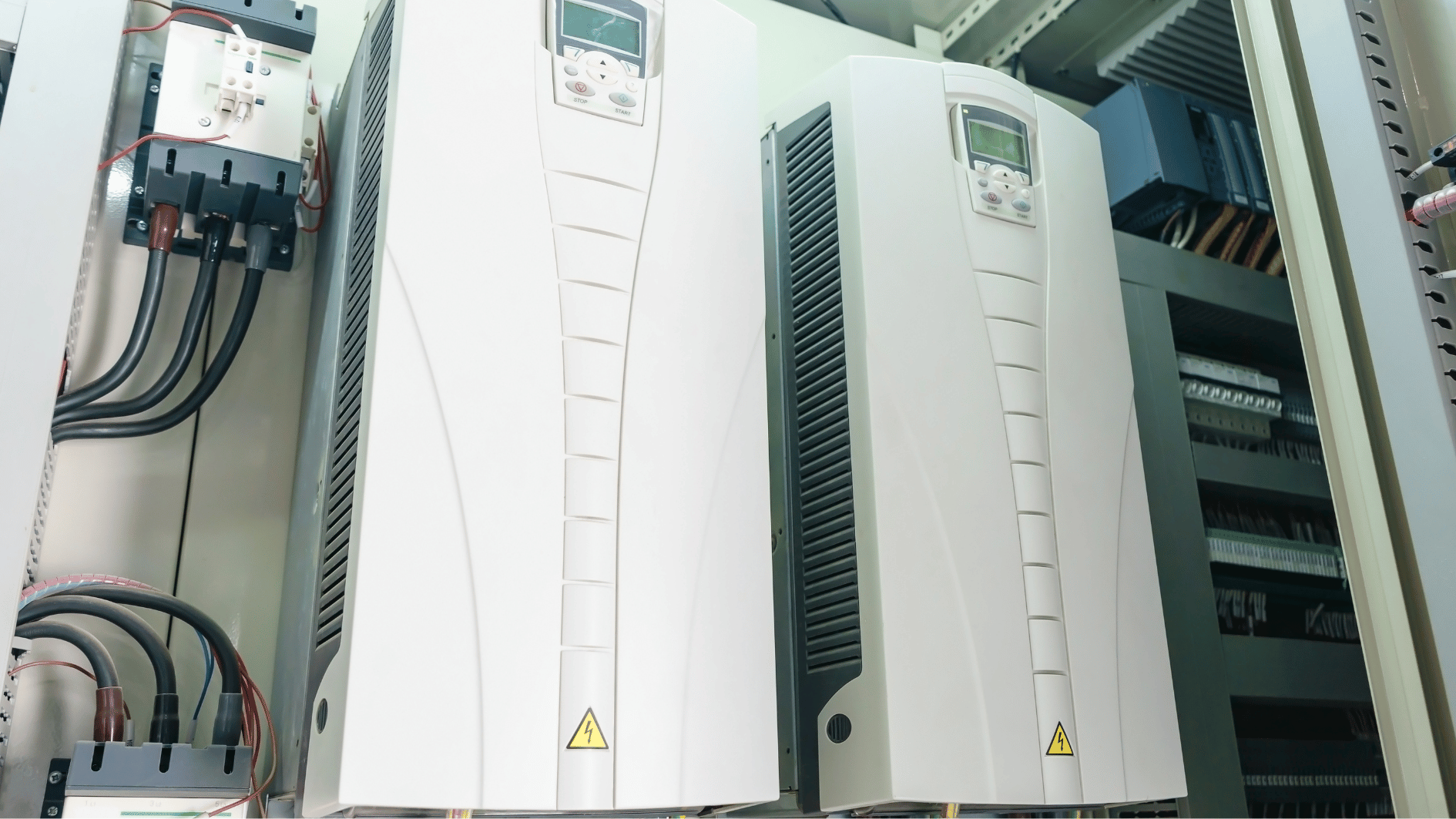
Image source: Canva.com
Off-grid solar power systems offer a reliable energy solution for remote locations, areas with unreliable grid access, or those looking to be energy-independent. Unlike grid-tied systems, off-grid solar setups are self-sufficient, requiring more robust components to ensure consistent power availability. One of the most critical components in an off-grid solar system is the inverter. This article explores the role of inverters in off-grid solar power systems, their functions, types, and the unique considerations involved in choosing the right inverter for an off-grid setup.
What is an Off-Grid Solar Power System?
An off-grid solar power system is an independent solar setup that generates, stores, and supplies electricity without relying on the electrical grid. It consists of solar panels to capture sunlight, a battery bank to store energy, charge controllers to regulate battery charging, and an inverter to convert stored DC power into usable AC power.
In these systems, the inverter plays a crucial role, converting DC power stored in batteries into AC power used by most household appliances. Additionally, many inverters designed for off-grid systems come with integrated functionalities that enhance system efficiency, reliability, and monitoring.

Exploring Off-Grid Solar
The Role of Inverters in Off-Grid Solar Power Systems
Converting DC to AC Power
Solar panels generate direct current (DC), which is stored in batteries. However, most household appliances and electronic devices operate on alternating current (AC). The inverter’s primary function is to convert this DC electricity into AC power, making it compatible with standard appliances. Without an inverter, an off-grid solar system could only power DC devices, which are limited in availability and often less efficient than AC appliances.
System Monitoring and Control
Many modern off-grid inverters come equipped with system monitoring capabilities. These inverters monitor the performance of the entire solar power system, including battery levels, solar input, and power usage. Users can view their energy consumption patterns, monitor battery health, and manage loads to ensure the system runs smoothly. Some inverters also offer remote monitoring, enabling users to keep an eye on their system from anywhere via a smartphone or computer.
Managing Battery Charging and Discharging
Battery management is crucial for off-grid systems, as overcharging or undercharging batteries can shorten their lifespan. Off-grid inverters are often combined with a charge controller, which regulates the charging process to protect the batteries. Many off-grid inverters are also designed to handle deep-cycle battery discharging, maximizing battery life by ensuring they’re not drained too low or charged too high.
Load Management and Power Prioritization
Off-grid inverters are often designed to manage different loads efficiently, ensuring critical appliances remain powered even during high demand or low energy generation. Some inverters can prioritize which devices receive power based on predefined settings, a feature called “load shedding” or “load prioritization.” For example, an inverter can ensure that essential appliances, like refrigerators or medical devices, are powered before non-essential ones.
Supporting Hybrid Systems and Backup Generators
Many off-grid inverters have the capability to integrate with backup generators or other energy sources, creating a hybrid system. This feature is especially useful for those in locations where solar energy alone may not be enough to meet demand year-round. When solar and battery power run low, the inverter can automatically switch to generator power, ensuring uninterrupted energy supply. This capability makes off-grid inverters versatile and suitable for areas with varying sunlight availability or unpredictable weather patterns.
Types of Inverters Used in Off-Grid Systems
Choosing the right type of inverter is essential for the efficiency, performance, and longevity of an off-grid solar power system. Here’s a look at some of the inverter options available for off-grid systems:
Pure Sine Wave Inverters
- Overview: Pure sine wave inverters produce an AC output that closely resembles the waveform of standard utility power. This type of inverter is suitable for sensitive electronics and appliances that require clean, stable power.
- Advantages: Pure sine wave inverters provide a consistent power supply compatible with all types of appliances, making them the preferred choice for off-grid systems.
- Considerations: Though typically more expensive than modified sine wave inverters, pure sine wave inverters offer higher efficiency and are less likely to damage sensitive equipment.
Modified Sine Wave Inverters
- Overview: Modified sine wave inverters produce a simpler AC output waveform, which is adequate for basic electronics but not ideal for more sensitive devices.
- Advantages: Modified sine wave inverters are generally more affordable and are suitable for basic appliances such as lights, fans, and simple electronics.
- Considerations: Because they provide a rougher waveform, modified sine wave inverters are not recommended for devices like refrigerators, medical equipment, or high-efficiency appliances, which may experience reduced performance or even damage.
Multi-Mode (Hybrid) Inverters
- Overview: Multi-mode inverters, also known as hybrid inverters, can operate both off-grid and in grid-tied modes. They are designed to work with battery storage systems and can switch seamlessly between solar, battery, and generator power.
- Advantages: Hybrid inverters are ideal for users who want a flexible system that can operate off-grid but may also connect to the grid or backup power sources when needed.
- Considerations: Multi-mode inverters are generally more expensive, but they offer greater flexibility and resilience in diverse power situations.
Key Considerations When Choosing an Inverter for Off-Grid Systems

Power Capacity and Sizing
The inverter’s power capacity should be carefully matched to the expected power demand. It should be able to handle the peak load of all devices that will run simultaneously. Under-sizing an inverter can lead to frequent shutdowns and inefficiency, while over-sizing can increase costs unnecessarily.
Battery Compatibility
Off-grid inverters need to be compatible with the type of battery storage system used (such as lithium-ion, lead-acid, or other battery types). Compatibility ensures proper charging and discharging, maximizing battery life and system efficiency.


Efficiency and Standby Power Consumption
Efficiency is critical in off-grid systems where every watt counts. Inverters with high conversion efficiency ensure minimal energy loss during the DC-to-AC conversion process. Some inverters also have low standby power consumption modes, which can save energy when the inverter is not actively converting power.
Monitoring and Remote Access
Modern off-grid inverters often come with built-in monitoring capabilities or compatibility with monitoring software. Being able to monitor energy production, battery status, and load consumption in real-time helps users manage power consumption and optimize system performance. Remote monitoring is especially beneficial for those who live far from their solar system, as they can keep track of system health from anywhere.


Durability and Weather Resistance
Since off-grid inverters are often installed in remote or outdoor environments, durability is essential. Look for inverters that are rated for weather resistance (e.g., IP65 or higher for outdoor use), and that are built to withstand temperature extremes and other environmental factors.
The Future of Off-Grid Inverters
As off-grid solar technology continues to develop, inverter technology is also evolving. Inverters are becoming more efficient, integrating better with battery storage, and including advanced monitoring and load management capabilities. Additionally, some newer inverters feature artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities, allowing them to optimize energy management autonomously based on consumption patterns and weather forecasts.
The integration of these features in off-grid inverters supports a more reliable, resilient, and user-friendly off-grid solar experience. As off-grid solar solutions become more popular in rural, remote, and disaster-prone areas, inverter innovation will remain at the forefront, ensuring sustainable, uninterrupted power for all.
In off-grid solar power systems, the inverter is a critical component that enables efficient energy conversion, system monitoring, and reliable power management. Users can ensure their off-grid system meets their energy needs with maximum reliability and efficiency by choosing the right inverter – whether a pure sine wave, modified sine wave, or hybrid model. Off-grid inverters are also advancing to include more robust monitoring and smart features, making them indispensable for anyone considering an off-grid solar setup. With the right inverter technology, off-grid solar users can enjoy the benefits of clean, self-sustaining power with the flexibility to adapt to future energy demands.





