Image source: Canva.com
As solar energy systems become more popular for residential and commercial use, understanding the different ways to integrate solar panels with battery storage has become increasingly important. One key consideration in designing an efficient and reliable solar power system is the choice between AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) solar battery coupling. Both methods have their unique advantages and can significantly impact the performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of your solar energy system.
AC and DC coupling refer to how the solar panels and battery storage are connected within the system. AC coupling is often favored for its flexibility and ease of installation, particularly in retrofitting existing solar systems. DC coupling, on the other hand, is known for its higher efficiency, especially in new installations where maximizing energy savings is a priority. This introduction will explore the benefits of each coupling method, helping you make an informed decision about which approach best suits your energy needs and goals. Whether you’re looking to enhance energy resilience, optimize efficiency, or reduce costs, understanding the benefits of AC vs. DC solar battery coupling is crucial in designing the most effective solar energy system for your home or business.
AC vs. DC Coupling: Explained
Solar panels generate DC electricity, which needs to be converted to AC electricity (used by most home appliances) through inverters. Solar batteries store electricity in DC form. The difference between AC-coupled and DC-coupled batteries lies in when the electricity from solar panels is converted from DC to AC before or after it’s stored in the battery.
In an AC-coupled system, DC power from solar panels goes to a solar inverter first, converting it to AC electricity. This AC power can then be used by home appliances or directed to a battery inverter, which converts it back to DC for storage. Therefore, in AC-coupled systems, solar electricity is inverted three times before being used if stored in the battery system.
In contrast, in a DC-coupled system, DC solar electricity flows directly from solar panels to a charge controller, which then feeds it into the battery system without converting it to AC. This means solar electricity is inverted only once (from DC to AC) as it flows from batteries to home appliances or the electrical grid.
Understanding Energy Storage Efficiency
A solar panel’s efficiency is its ability to convert sunlight into solar energy, while a solar inverter’s efficiency measures how effectively it converts this solar energy into usable AC electricity. Battery efficiency, however, is more nuanced.
Most solar batteries are rated based on roundtrip efficiency, which gauges the amount of electricity lost during charging and discharging cycles. Higher efficiency percentages indicate better conversion of incoming electricity into stored energy and back into usable electricity. For instance, a battery with 80% roundtrip efficiency means that out of 10 kilowatt-hours (kWh) sent for storage, 8 kWh can be retrieved for use.
AC Coupling
AC-coupled solar battery systems excel in ease of installation, particularly when retrofitting storage to an existing solar setup. Simplified installations require less labor and time, typically resulting in lower upfront costs.
Moreover, both solar panels and the grid can charge batteries in AC-coupled systems. Being grid-tied allows flexibility – if solar PV production isn’t sufficient to fully charge the battery, the grid can supplement.
However, AC coupling involves multiple AC-to-DC and DC-to-AC conversions, leading to minor efficiency losses.
DC Coupling
DC-coupled solar systems boast higher efficiency compared to AC-coupled counterparts. Unlike AC systems, which convert electricity between AC and DC three times, DC systems perform only one conversion from solar panels to battery storage, enhancing efficiency.
Nevertheless, DC coupling is more complex to install for retrofit storage, potentially increasing upfront costs and installation time. Additionally, DC-coupled batteries may not qualify for certain utility storage programs aimed at generating revenue.
Historically, AC-coupled setups have been more common in residential and commercial solar installations. However, DC-coupled solar batteries are gaining popularity as more options become available.
Choosing the Right Solar-Plus-Storage System Setup
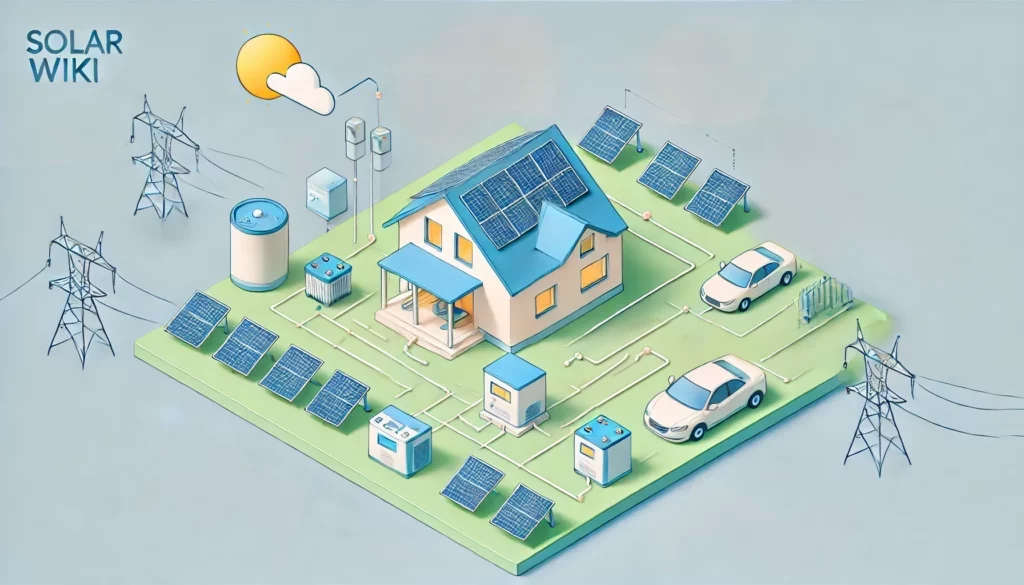

If you already have a home solar array and plan to add an energy storage system as a retrofit, an AC-coupled setup is likely the best choice. This is because you already have a solar inverter system in place, and switching to a DC-coupled system would involve complex rewiring, potentially increasing installation costs.
On the other hand, if you’re installing solar panels and a battery storage system simultaneously, a DC-coupled configuration may offer higher overall efficiency. However, note that DC-coupled systems tend to be more complex to install, which can impact upfront costs.
Explore a wide variety of batteries available on SolarWiki to find the perfect match for your solar energy system. Visit SolarWiki batteries page and discover the best options to power your home efficiently!