Image source: Canva.com
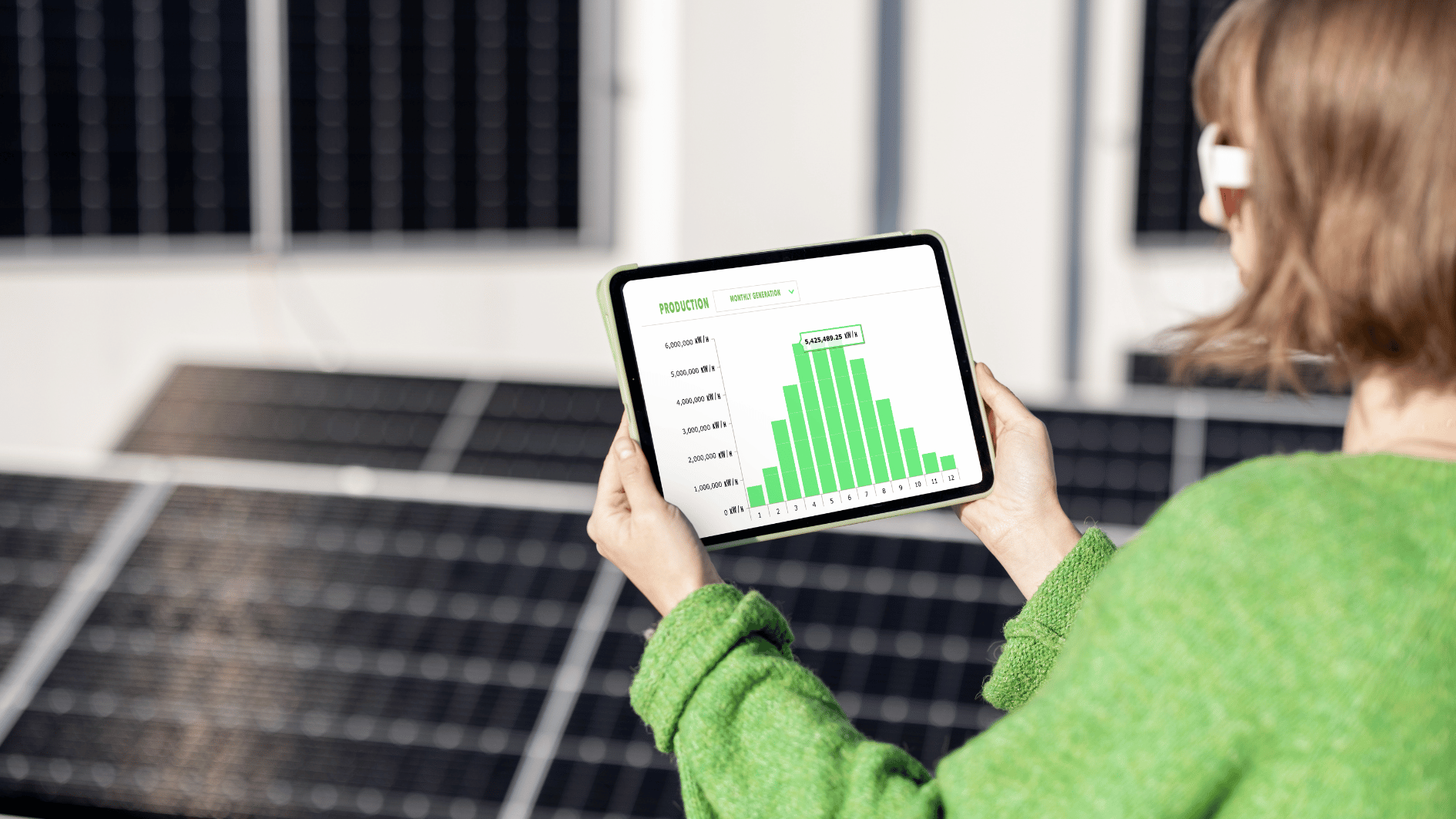
To get the most out of your solar panels, consider investing in a solar monitoring system. This technology provides real-time tracking of your energy production and usage, eliminating the need for guesswork about your system’s performance. It also alerts you to any drops in output or issues with panels, batteries, or other components.
Many top-rated solar companies offer solar monitoring systems. We’ve researched the leading options to help you understand their features and benefits. After installing a high-performing residential solar system, a monitoring system will ensure you stay informed about its health and efficiency.
How Solar Monitoring Systems Operate
Solar monitoring systems utilize sensors and communication devices attached to your solar panels. These sensors, often built into the inverter, track production data from each panel, including voltage, current, and power output. This data is then transmitted to a communication device, such as a gateway, which sends it to cloud-based software via Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or a cellular network.
Homeowners can access system information through a dedicated web portal or mobile app. Most systems present this data through visualizations like bar graphs and charts. You’ll be able to view power production rates for each panel, daily energy production, historical trends, and details about your energy usage. This allows you to compare your home’s power consumption and peak usage periods with the energy generated by your system, helping you manage and optimize energy use. Additionally, for those with solar batteries, you can also monitor and optimize charging and discharging cycles.
Beyond real-time data, many systems provide proactive alerts for any issues, such as system faults or drops in power production. Some even offer weather alerts for low-sunlight days or approaching storms. These features help you quickly address problems, minimize system downtime, and plan for emergencies, ensuring you have efficient stored solar power when you need it.
Types of Solar Monitoring Systems

There are three main types of solar monitoring systems available from equipment manufacturers, professional installers, and third-party companies. Here’s a breakdown of each:
1. Equipment-Integrated Solar Monitoring
Solar manufacturers often offer monitoring systems built directly into their equipment. This can be integrated into either the solar panels or the inverter, which converts DC power from the panels into AC power for your home. Inverter-based monitoring systems are more common and generally provide easy-to-read data through a website or mobile app.
Inverter-Based Monitoring
Tracks energy production, basic home energy use, and overall system performance. Inverter systems may use string inverters (connected to multiple panels) or microinverters (attached to individual panels). Microinverters offer module-level monitoring, showing the performance of each panel.
Built-in Software
Typically included with the inverter and compatible with many solar panel brands. Advanced features like module-level monitoring may incur additional costs.
2. Installer Solar Monitoring
Some solar installers provide their own monitoring apps alongside their installations. These apps enhance and customize the data from your inverter’s built-in monitoring, offering insights into daily production, upcoming electric bills, and online payment options.
Features
Installer apps often include clear insights, support for troubleshooting, maintenance scheduling, and local weather alerts. Data is usually accessible through a dedicated website or mobile app.
Limitations
May not offer the detailed, module-level data available with some dedicated systems.
3. Third-Party Home Energy Monitors
Third-party monitoring systems, from companies not involved in solar equipment manufacturing or installation, focus on your entire home’s energy usage rather than just solar. These systems use current transfer (CT) sensors to monitor energy flow and can track major appliances or integrate with smart home devices.
Features
Provide cost analysis, historical trends, customizable goals, alerts for unusual energy spikes, and sometimes estimates of greenhouse gas emissions. They work alongside existing solar monitoring systems and may offer solar-specific features.
Installation
Professional installation by an electrician is recommended for safety and proper setup, although some systems are designed for DIY installation. Always follow product instructions closely.
Each type of system offers unique benefits and insights, so choose one that best fits your needs for monitoring and optimizing your solar energy use.
How to Choose a Solar Panel Monitoring System

Accessibility
Determine if you need web access, a dedicated app, or both. Choose a system with a user-friendly dashboard or interface for easy navigation and monitoring.
Alerts and Notifications
Opt for a system that provides timely, customizable alerts for performance issues, local weather conditions, or system malfunctions.
Compatibility
Ensure the monitoring system is compatible with your existing solar panels and inverters. Some systems work only with specific brands, so verify compatibility before purchasing.
Data Reporting
Look for a system that offers real-time data on energy production, consumption, and historical trends. Up-to-date information helps maintain peak performance and maximize energy savings.
Overall Cost
Be aware of any recurring costs for cloud backup or data analysis. Granular production details may require additional sensors, with standalone monitoring systems typically costing around $300, potentially more with extra equipment.
Troubleshooting and Support
Choose a system with reliable technical support and troubleshooting options. Access to an online knowledge base or manual can also be beneficial.
Evaluate these factors based on your specific needs to select the most effective monitoring system for your solar panels.
Solar monitoring systems help maintain peak performance for your solar panels. These systems often come integrated with your solar inverter or are provided by your installation company, though availability can vary based on your system’s setup and installer. Stand-alone energy monitors can offer detailed insights into your power production, but they may require additional sensors to fully integrate with your existing system.