Back to: Innovations in Solar Panel Technology
Solar panel technology has come a long way since its inception in the 1950s. Understanding the history and evolution of solar panels provides valuable context for appreciating modern innovations. This lesson covers the technological milestones, key challenges, and breakthroughs that have shaped the solar industry.
Key Points:

First-Generation Solar Panels:
- Introduced in the 1950s, using silicon-based photovoltaic (PV) cells.
- High production costs and low efficiency (~6%).
- Initially used in space applications due to their reliability.
- Early adopters faced challenges with scalability and affordability.
Second-Generation Solar Panels:
- Thin-film technology emerged in the 1980s.
- Made from materials like cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and amorphous silicon.
- Lower production costs but also lower efficiency (~10-12%).
- Flexible and lightweight, making them suitable for various applications, including portable solar devices.

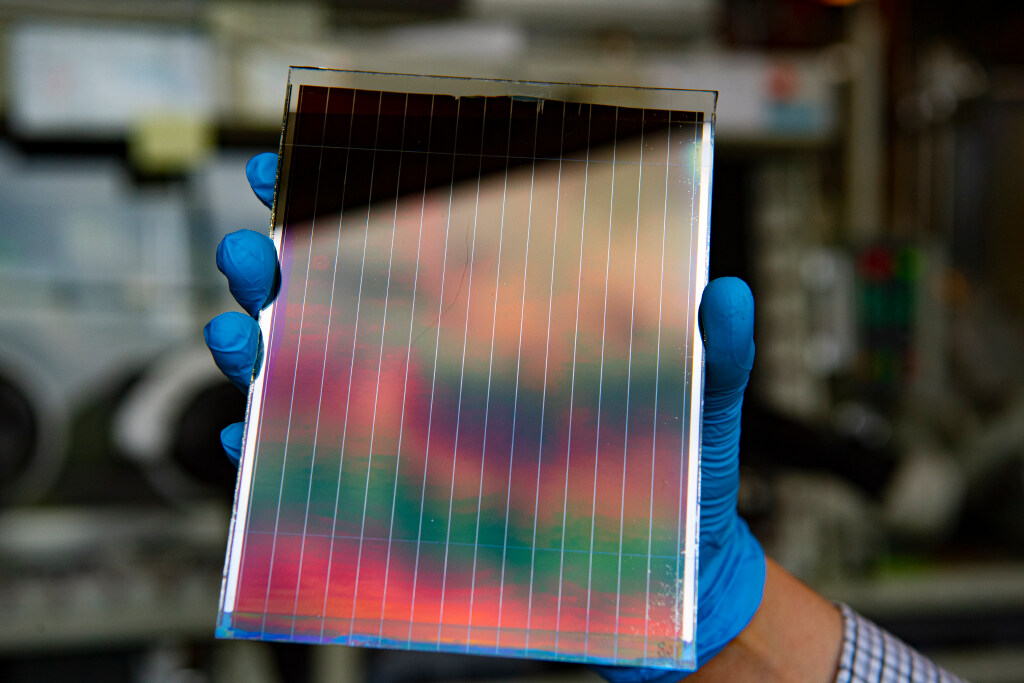
Third-Generation Solar Panels:
- Incorporate advanced materials like perovskite, organic PV cells, and dye-sensitized solar cells.
- Focus on flexibility, lightweight designs, and higher efficiencies.
- Current research pushing efficiencies beyond 20% with reduced costs.
- Addressing challenges like material stability, environmental impact, and mass production scalability.